EML4-ALK kinase inhibitor 1
CAS No. 1373409-08-5
EML4-ALK kinase inhibitor 1( EML4 ALK kinase inhibitor 1 )
Catalog No. M26196 CAS No. 1373409-08-5
EML4-ALK kinase inhibitor 1 is a potent oral active inhibitor of echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (EML4-ALK), with an IC50 of 1 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 335 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 500 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 806 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1098 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1485 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 2961 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameEML4-ALK kinase inhibitor 1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEML4-ALK kinase inhibitor 1 is a potent oral active inhibitor of echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (EML4-ALK), with an IC50 of 1 nM.
-
DescriptionEML4-ALK kinase inhibitor 1 is a potent oral active inhibitor of echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (EML4-ALK), with an IC50 of 1 nM.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsEML4 ALK kinase inhibitor 1
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorLp-PLA2
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1373409-08-5
-
Formula Weight580.778
-
Molecular FormulaC31H48N8O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 110 mg/mL (189.41 mM)
-
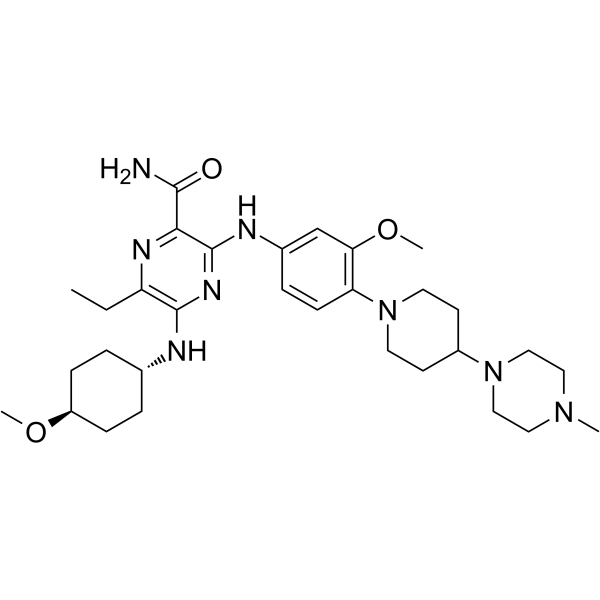
SMILESCCc1nc(C(N)=O)c(Nc2ccc(N3CCC(CC3)N3CCN(C)CC3)c(OC)c2)nc1N[C@H]1CC[C@@H](CC1)OC
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Zehong Wan, et al. Bicyclic pyrimidone compounds. WO2013014185A1.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ansamitocin p-3 B
Ansamitocin p-3 (Maytansinol isobutyrate) is an inhibitor of microtubule with IC50 of 3.4 μM for tubulin polymerization.
-
Bicyclo[5.3.0]Decape...
Bicyclo[5.3.0]Decapentaene is a natural product.
-
SJ6986
SJ6986 is a chemical probe for studying the role of GSPT1/2 in vitro and in vivo. SJ6986 supports the utility of a diverse library of CRBN binders in the pursuit of targeting undruggable oncoproteins.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


